Understanding breast cancer
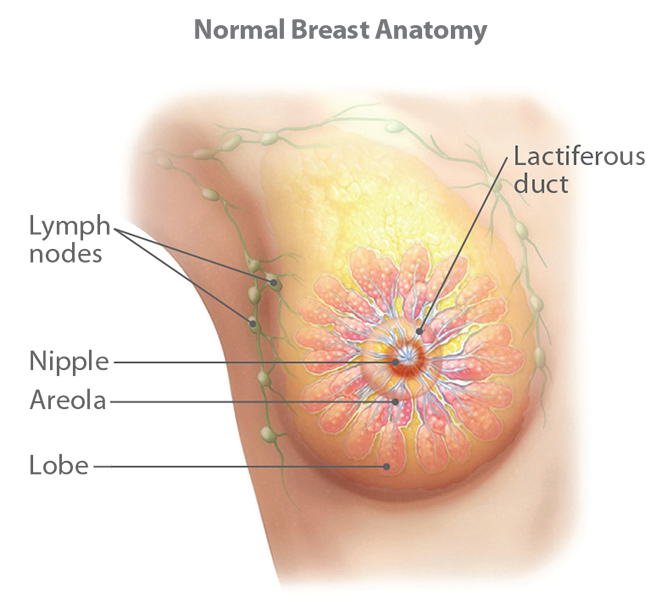
Breast cancer is cancer that forms in cells of the breast. The breast consists of lobules (glands that make breast milk), ducts (small tubes that carry milk from the lobules to the nipple), fatty and connective tissue, blood vessels and lymph vessels.
The milk-producing ducts and glands are the two most likely areas to develop cancerous cells. In rarer cases, breast cancer begins in fatty tissues, also known as stromal tissues. Breast cancer may also occur in surrounding lymph nodes, especially those of the underarm.
Types of breast cancer
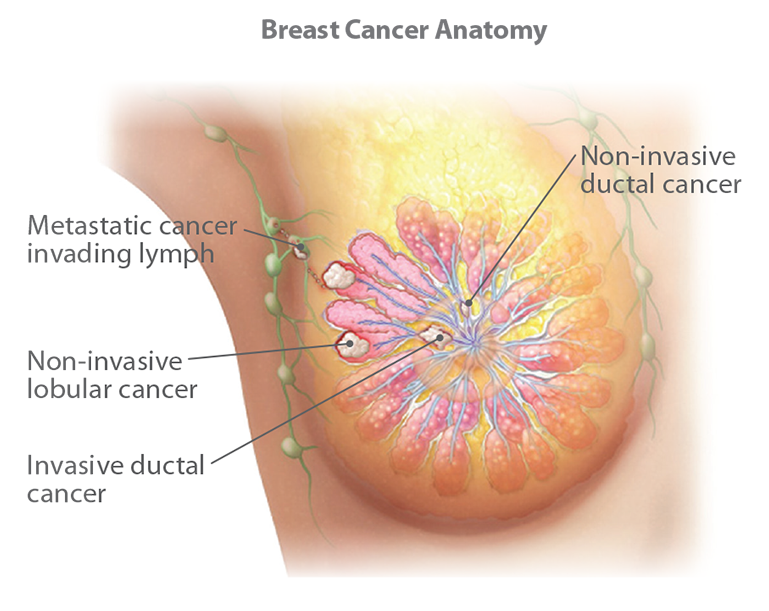
Breast cancer occurs in two broad categories: noninvasive and invasive.
Noninvasive (in situ) breast cancer: Cancerous cells remain in a particular location of the breast, without spreading to surrounding tissue, lobules or ducts.
Invasive (infiltrating) breast cancer: Cancerous cells break through normal breast tissue barriers and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymph nodes.
Stages of breast cancer
The stage of breast cancer is one of the most important factors in evaluating your treatment options.
Stage 0 (noninvasive, carcinoma in situ) breast cancer
In stage 0, there is no evidence of cancer cells breaking out of the part of the breast in which they started, or of getting through to or invading neighboring normal tissue.
Stage 1 (invasive) breast cancer
In stage 1, the tumor measures up to two centimeters and no lymph nodes are involved.
Stage 2 (invasive) breast cancer
In stage 2, the tumor measures between two and five centimeters, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer.
Stage 3 (locally advanced) breast cancer
In stage 3, the tumor in the breast is more than two inches in diameter and the cancer is extensive in the underarm lymph nodes, or has spread to other lymph nodes or tissues near the breast.
Stage 4 (metastatic) breast cancer
In stage 4, the cancer has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast.
Recurrent breast cancer
In recurrent breast cancer, the disease has returned in spite of the initial treatment.